Windows Petzold , VB , COM , .NET the technology shift of Microsoft has been evolved or should I say innovative ways to adapt to industry trend. Now we are at a yet another paradigm shift we call it a Cloud.
This post is more oriented towards next gen application on public cloud.
The Cloud is adding an element into the DNA of the App Development. With this new paradigm the App Dev has be relooked into on various aspect, Below is a compilation of the some of the areas.
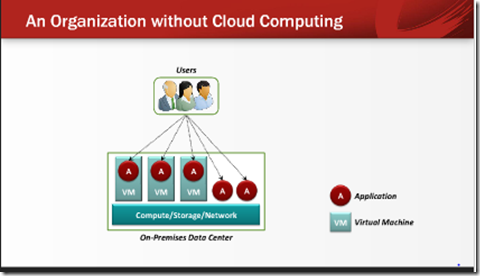
1) There is more to Cloud: The cloud is here most of the people think about cloud as Windows Azure or Office 365 or Amazon AWS there is not reason I cannot see why a customer in 5 years from now buy a customized data center with pre loaded application . The story for cloud is vast.
2) BI (Business Intelligence)
The developer is the key in Windows 8 but we need to concentrate on the back end applications. BI is an important game changer here. The next wave of smart apps are insightful, inside fueled applications. We need to get the fundamentals in place for the same.
- Data is happening
Data is again a big area and its happening “Google ingest 10Petabyte / month”, so is bing so much of data to analyze and give better search results. There is so much of Data all over the place, Big Data is happening (Big Data will be covered in a different post.
3) Latency
In the cloud world latency has a totally paradoxical definition for example: A web application which runs on cloud is not necessarily going to have the database tier in the same cluster as app for all practical purpose the application can be hosted on a different fabric & database tier be it Sql Azure or Amazon RDS could and expectation of a millisecond response from the app to the database tier is irrational. So in principle applications have to be rewired with the asynchronous paradigm to really get going in cloud. On an alternative note “Australian Stock Exchange on cloud has a requirement of have trade placement done in 7 micro seconds. Latency on one side is becoming shorter on one side and other side it can be really long.
3) Application Life Cycle Management (ALM)
This is a big theme within App Dev. Application Lifecycle Management for cloud based application changes and need to look into some very specific areas.
- User Experience
User Experience has never mandated to be more innovative easy to use “a classic example is Apple I Pad 55% of users of IPad in US are senior citizens. So this gives a sense the Apple has set some very high standards. UX in collaboration with mobility can really may a key difference. Mobility bring real time knowledge in terms intelligence of Location. Applications are no more isolated they are more of connected entities which learn from information provided by other application and help in making the end user experience more richer and innovative. Its time that UX is proactively thoughts.
- Identity
For Identity Management in Cloud the mantra is to use the defacto standard LDAP, Active Directory.
- SDL
Security Development Lifecycle, the important aspect here is the concept of privacy. In public cloud application need to have a strategy in terms of how to deal with PII (Personal Identifiable Information). Its mandate to declare to users what is the information which is stored about them on the cloud. Another important aspect in case of an security breach how does the messaging go over to the end user.
- Testing
Testing Strategy for cloud application needs to be rethought. Debugging in cloud is a lot different especially in a case of 24X7 systems.
- Manageability & Operation
Very much based on ITIL. All cloud providers datacenters use ITIL or enhanced form of ITIL to manage. From an application developer stand point what does manageability mean to his/her application, “Application have to be build some manageability to function properly in a cloud based environment.
Cloud based application architecture mandate the theme of reusability to a high degree we live in asynchronous world (cloud) & we require a certain degree of standardization of applications being component & service oriented compliant. The drive to build reusable components in cloud can help faster deployment of applications into cloud. Doing it right is really what matters now unless companies don’t wont go down the path of rewriting cloud application in next 3 years time frame.
4) Fabric Based Computing
Azure is an SOA based infrastructure what we have done in last 10 years is what we see packaged all in Azure. Lets take azure with a pinch of salt what we have on premise application lets not oversell telling the customers that on cloud we are going to great benefits.
“Fabric-based computing is the next-generation architecture for enterprise servers. It combines powerful server capabilities with advanced networking features into a single virtual server configuration. In fabric-based computing, resources are no longer tied to a specific physical machine. They can be reconfigured on the fly without adding software layers. Everything is done at the hardware level (CPU memory, network I/O, etc.). Reconfiguration doesn’t happen at the individual machine level but at the ‘fabric’ level,”. What does this mean to application placed on the public cloud? We are typically talking about PAAS. Fabric is computing is essentially where it is required to manage 1 to n servers, we should able re purpose virtual machines or workload resources at any point time and use the same for something different without having to think about it.
5) Architecting For Cloud: As we move into a stateless world and asynchronous modalities across all layers, the architectural discussion on cloud re-opened up for big debate what would a starting point be for an architect really be when he/she is migrating an existing application to a cloud. The slide gives a flavor on what would an architect really start pondering on. Where does the Architect start?
Decompose application by Functions: First Principle “Decompose application by Functions example : Order Management.”
The requirement here is to build flexible components that understand how to work on multiple resources, essentially cloud is one big pool of resource, we call it the fabric.
We start with Infrastructure which is the fabric. Going back to Fabric which is a pool of resources where the cloud application is deployed.
For example the Inventory Application the Inventory System(App Fabric) is a fabric which is drawn on by structuring the components in line of stateless app , process and database. The first level optimized is done at application fabric level.
The Inventory System Fabric in turn talks to the Infrastructure Fabric for resources.
Fabric is a pattern of computing architects have to start thinking about & that’s what the cloud is all about.
Windows Server is doing a lot of work around the same.
As application developer we need to starting thinking about virtual machines, resilience, elasticity & homogenize resources as key concepts.
Azure is elastic in itself for its resource if your application is written in a monolithic manner God Save you, you as the developer needs to design & code for elasticity. The important message is to learn the principles.
Decompose function by roles: example web role, worker role , database role , integration … cont’d in next section.
6) Asynchronous Paradigm
Azure is designed for load balanced, stateless in the middle tier and state tier, we assume that components can be killed at any moment assuming the fabric controller is doing an optimization algorithm and considering you have more then one instance, so a lot of out design points like putting things into registry, settings, color schemes, file system in a the new bad design principle in cloud.
Azure doesn’t do squat for you on elasticity if your applications are not composable and cannot put the application on top of multiple tiers it’s a bad design.
That’s why we come to composition by function and then roles. Functional Decomposition is not by functions and then roles.
You can scale the tier individually. There is whole bunch of things which is abstracted based on roles for example web role will have IIS and worker role has TCP/IP as the base communication standard.
Asynchronous paradigm brings a new problem to the database example “ you are doing a ticket reservation on an application on the cloud you commit the transaction so how do you write to the database non relational does it wait all the memory or write back immediately another design change. There have to buffers put in the system to protect the database. No Sql is the new mantra for the database for cloud. While this may sound exciting but a lot of discussions needs to understand what does it mean to an application developer, this will be covered in a separate post.
7) Management of Cloud Applications
Cloud applications are automated application and so is the monitoring and management needs zero human intervention that’s where we are getting to.Landscape of Monitoring and Management is really large now…..
8) Insightful & Adaptive Applications
People ready Application is something on the lines of Windows 8 Metro or iPad. There is need to design for different form factors with different environment. HTML 5 can solve some problem but conditional aspect like speed , bandwidth need to paid attention. Know your users better and give them what they are looking or will look at a future date or will be productive to the user.
The Last word on this Post Private Cloud is nothing but a Mainframe………..
Next Post on Big Data…….